- The most threatening problem for the Union from 1861 through 1863 was:
- refusal of several northern states to allow conscription
- French and Spanish objections to the Union blockade of Confederate ports
- border states wavering between loyalty to the Union and secession
- possible British recognition of the Confederacy
- Congressional Reconstruction ended in 1877 because:
- the freed slaves had been successfully integrated into southern society
- Radical Republicans officially relinquished political power to southern Democrats
- most of the politically active black people had left the South for northern cities
- Democrats and Republicans effected a compromise regarding the 1876 presidential election
- The most notable foreign affairs issue that faced the United States between the announcement of the Monroe Doctrine and the Civil War was:
- securing international recognition from governments of Europe
- defining the nation's northern and southern boundaries
- the political instability of several Spanish holdings in Central America
- British warships patrolling the Great Lakes
- During the 1850s, the South differed from the North in that the South:
- had a better-educated white population
- was less interested in evangelical religion
- had a more extensive transportation system
- attracted fewer European immigrants
- The Kansas-Nebraska Act heightened the sectional crisis because it:
- validated the controversial Dred Scott decision
- repealed a key portion of the Missouri Compromise
- barred slavery in both future states of Kansas and Nebraska
- challenged the constitutionality of the Gadsden Purchase
- The failure of the South to create a flourishing industrial economy prior to the Civil War was partly the result of a/an:
- unwillingness by southerners to take business risks
- slave labor force unable to transition from agriculture to manufacturing
- value system throughout the South that frowned on urban and industrial growth
- lack of business prowess among southerners
- "July of 1863 marks the pivotal juncture of the Civil War. Confederate General Robert E. Lee made a bold decision to penetrate Union soil. After three days of horrific battle, the Army of the Potomac, under command of General George Meade, forced the Army of Northern Virginia into retreat. It was Lee's first defeat of the war. Meanwhile, another Union victory, coupled with success at Port Hudson in Louisiana, isolated Arkansas, Louisiana, and Texas, thus giving the North complete control of the Mississippi River. Additionally, it led President Abraham Lincoln to recognize the military leadership prowess of General Ulysses S. Grant, subsequently appointing him commander of all Union forces." The two crucial engagements described
are:
- Fort Sumter and Bull Run
- Shiloh and Chancellorsville
- Gettysburg and Vicksburg
- Cold Harbor and the Wilderness
- At the outset of the Civil War, southerners held all of the following expectations except:
- the materialism of the North would prevent it from fighting an idealistic war
- Great Britain would intervene on behalf of the South in order to preserve its source of cotton
- northern unity in the struggle against the Confederacy would eventually dissolve
- the economic and military resources of the South would outlast those of the North
- The statement that best describes how the Civil War affected the American economy is:
- "the enormous number of Civil War casualties created severe labor shortages and effectively stifled economic growth"
- "the country's economic prosperity was crippled by the wanton destruction of material resources during the Civil War"
- "the Civil War led to the beginnings of the military-industrial complex"
- "by speeding economic change the Civil War helped prepare the way for modern industrial society in America"
- The position of the Republican Party during the 1850s regarding slavery was that:
- national slavery should be abolished by congressional action
- individual territories should decide the issue by process of popular sovereignty
- slavery could remain where it already existed but should not be extended into new territories or states
- the issue should be solely determined at the state level without federal interference
- Southern blacks who fled the violence of Reconstruction in 1879 and 1880 to start anew in Kansas were known as:
- exodusters
- scalawags
- jayhawkers
- copperheads
- President Abraham Lincoln fought the Civil War to:
- punish the South for its many years of transgressions against blacks
- stabilize the economy, suffering the effects of uncooperative southern planters
- abolish slavery in the United States
- preserve the Union, threatened by secession of numerous southern states
- The position least supported by the American Colonization Society, founded by northern religious reformers in 1817, was:
- gradual emancipation of slaves
- compensation to owners of freed slaves
- deportation of all free blacks for resettlement in their African homeland
- strong opposition to racist laws and customs in the United States
- The most controversial and divisive component of the Compromise of 1850 was:
- New Mexico Territory and Utah Territory were organized under the mechanism of popular sovereignty to determine the question of slavery
- the Fugitive Slave Law of 1793 was amended to provide for more stringent action against runaway slaves
- California was granted admission to the Union as a free state
- slavery was not banned in the District of Columbia
- The statement that best expresses the principle of "popular sovereignty" is:
- "settlers in a given territory have the sole right to decide whether or not slavery will be permitted there"
- "citizens can decide each for themselves whether or not to hold slaves"
- "Congress has the right to determine where slavery shall and shall not exist"
- "individual states have the right to reject congressional decisions pertaining to slavery"
- All of the following led to northern fear of a slave power conspiracy in the 1840s and 1850s except:
- the Wilmot Proviso
- modifications of existing fugitive slave legislation
- the Dred Scott decision
- proposal of the Ostend Manifesto
- Between 1810 and 1860, the South's slave labor force increased dramatically due to:
- growth in the African slave labor trade
- the emergence of King Cotton
- natural population increase of American-born slaves
- the recent acquisition of Louisiana from France
- The single-most impacting event that convinced many white southerners they could no longer prosper in the Union and to therefore move toward secession was:
- the assault on Senator Charles Sumner by Congressman Preston Brooks
- the Kansas-Nebraska Act
- John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry
- the election of Abraham Lincoln to the presidency
- The Battle of Antietam is considered pivotal to the outcome of the Civil War because it:
- marked the first use of black troops by the Union
- forestalled the possibility of European intervention
- effectively split the Confederacy by isolating Florida and Georgia
- represented the Union's deepest thrust into southern territory
- Black narratives suggest that slaves considered the worst aspect of slavery to be the:
- physical pain they suffered from whippings and beatings
- shoddy and unsanitary conditions in which they were forced to live
- psychological trauma of being considered inferior to whites
- overall coercion and lack of freedom in their lives
- The Missouri Compromise was a victory for antislavery advocates because the measure:
- closed most of the Louisiana Territory to slavery
- provided for gradual emancipation of slaves in all states west of the Mississippi River
- effectively nullified the Fugitive Slave Act
- prohibited slavery in all future territorial acquisitions
- The statement that best describes the extent of "Negro rule" in the South during Reconstruction is:
- "blacks played a significant role in the politics of several states but never managed to elect a governor or control a state legislature"
- "while some blacks held local and state elective offices, their impact was minimal throughout the South"
- "in the Deep South, where blacks constituted a voting majority due to disenfranchisement of vast Confederate supporters, blacks dominated state politics"
- "blacks did not actually achieve many elective offices, but as prominent citizens and community leaders, they aligned with white Republicans to effectively control politics in all but three of the former Confederate states"
- The southern economy before the Civil War increasingly:
- produced more rice, sugar, and tobacco and less cotton
- flourished as a result of high tariffs and availability of immigrant labor
- diversified with more manufacturing-based industry and mechanized agriculture
- relied on cotton production supported by slave labor
- Of the following, the one which occurred during Radical Reconstruction is:
- formation of the Ku Klux Klan
- general assimilation of emancipated blacks into southern society
- widespread redistribution of confiscated plantation land to former slaves
- creation of a new industrial base in several southern states
- The Dred Scott decision:
- stated that blacks were not citizens, hence they had no legal access to federal courts
- upheld the constitutionality of the Missouri Compromise
- refused to free Dred Scott, but recognized the power of Congress to legislate slavery
- supported the principle of popular sovereignty
- A major economic development in the South during Reconstruction was the:
- decline of the textile industry
- formation of large commercial and banking centers
- pinnacle of the cotton industry
- onset of runaway inflation
- During the final months of the war, the South was defeated largely due to:
- simple attrition of southern fighting forces
- internal rebellions in some of the northernmost Confederate states
- superior military leadership and strategy of the North
- lack of adequate financing to continue the war
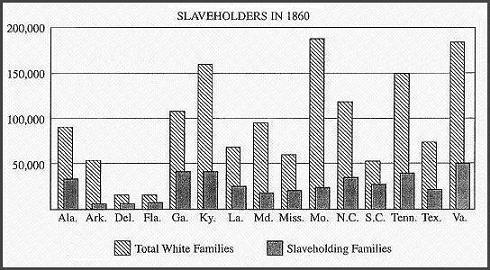
- All of the following statements are false. The bar graph above directly refutes the assertion that:
- "the South was more populated than the North"
- "there were more blacks than whites in the antebellum South"
- "most southern families owned slaves"
- "the majority of southerners were urban dwellers"
- In the last half of the nineteenth century, the New South advocates supported:
- cooperation between North and South to integrate the freed blacks into society
- development and expansion of southern industry
- elimination of Jim Crowism
- ratification of the Fifteenth Amendment
- After the Civil War, women reformers and former abolitionists were divided over:
- development of the sharecropping system throughout the South
- use of military force to maintain order in the South
- dependence on female workers in northern factories
- national legislation that ensured voting rights of blacks
- The Black Codes enacted in various southern states after the Civil War were intended to:
- gradually dissipate racial prejudice and create opportunities for freed slaves
- promote the return of former slaves to Africa
- enable black citizens to vote in federal elections and eventually hold office
- limit the socio-economic status blacks in the face of Radical Republican measures
- The "positive good" defense of slavery was based on all of the following suppositions except:
- enslavement was the natural and proper status for people of African descent, since they were innately inferior to whites
- slavery was sanctioned by Christianity (the Bible contains several passages of Paul urging servants to be obedient to their masters)
- as "perpetual children," blacks were naturally dependent and therefore in need of an environment that provided almost constant supervision
- the South's master-slave relationship was often more humane than what existed between employers and wage laborers in the North
- The key factor in Great Britain's decision to reject Confederate expectations of a British declaration of war against the United States was the:
- public pressure exerted on Parliament by the mass of common people in Great Britain who favored the North
- clearly emerging battlefield superiority of the North
- brilliant diplomacy of Charles Francis Adams, who served as American minister in London throughout the Civil War
- unexpected need for northern wheat, rather than southern cotton, due to crop failures in Great Britain
- The practice of religion amongst the slaves generally:
- reflected the form of Christianity practiced by the plantation owners and neighboring whites, with earthly sinfulness and fear of damnation as core themes
- offered an opportunity for natural leaders within the slave community to emerge
- rejected their African religious customs and cultural roots
- focused on prayer that God would someday grant each individual slave the needed courage for open rebellion and the chance for escape to freedom
- The New York City draft riots in July of 1863 were triggered in part by:
- racial backlash against the Emancipation Proclamation
- frustration with rampant inflation and stagnant wages
- few battle victories compounded by heavy casualties
- anger over war profiteering by unscrupulous businesses
- The Emancipation Proclamation did not:
- establish that the Civil War was henceforth being fought not just to maintain the Union, but to eliminate slavery as well
- serve as propaganda to convince free northern blacks to join the Union ranks, and spur many slaves near Union lines to desert their plantations
- provide the necessary legal foundation to punish Confederate military officers and government officials when the war was over
- help dissolve British support for the Confederacy
- During the Civil War, the Republican Party passed legislation to promote economic development concerning all of the following except:
- granting government subsidies to encourage export of manufactured goods
- distribution of free western land to homesteaders
- establishing a high tariff to protect American industry from foreign competition
- providing land grants to coax private railroad companies into undertaking construction of a transcontinental railway
- The primary objective of the founders of the "Know-Nothing" Party was:
- formation of military alliances with foreign powers
- abolition of slavery
- restriction of the rights of immigrants
- improvement of factory working conditions

- The above drawing, which appeared in the Tuscaloosa (Alabama) Independent Monitor in 1868, issued a stern warning to:
- carpetbaggers and scalawags
- Radical Republicans
- slaves and "undesirable" immigrants
- Ku Klux Klan members
- The common thread in the Slaughterhouse Cases of 1873 and Civil Rights Cases of 1883 is that the Supreme Court rulings:
- concerned complicated legalities involved in implementation of the Emancipation Proclamation
- were essentially reversed in Plessy v. Ferguson (1896)
- undermined protections granted to blacks under the Fourteenth Amendment
- were widely denounced by southern political leaders
- Historians generally agree that the deepest failure of Reconstruction was the inability to:
- convince preferred European trade partners that the United States was economically healthy
- integrate the freed black slaves into society dominated by white Americans
- revive the southern economy and merge it with that of the North to promote a flourishing national economic system
- soften the country's hardened geographical allegiance to political parties
|