- Shays's Rebellion reflected the nation's internal tension during the 1780s regarding:
- conflict between Loyalist supporters of Great Britain and those colonists who favored independence
- economic frustration of New England farmers who had difficulty paying debts in hard currency
- rivalry between merchants and shipbuilders in the Carolinas
- government restrictions on westward expansion into the Ohio Valley region
- The first major challenge to President George Washington's Proclamation of Neutrality issued in 1793 originated from:
- Great Britain, which failed to send diplomats to the United States following the overbearing Jay Treaty of 1795
- Citizen Edmond Genêt, who solicited American support for France in its war against Great Britain and other European nations
- western expansionists who formed a sizable militia to invade and annex portions of Canada adjacent to the Great Lakes
- Spain's refusal to abide by the Pinckney's Treaty regarding navigation rights on the Mississippi River and port provisions at New Orleans
- Of the following, the person who most likely would have associated the concept of "democracy" with the statement "government by passions of the multitude" is:
- George Washington
- Thomas Jefferson
- Alexander Hamilton
- John Adams
- The Louisiana Purchase was significant because it:
- virtually eliminated Spain from the North American continent
- gave the United States control of the Mississippi River
- forced the British to evacuate their posts in the Northwest
- eased tensions between western settlers and Indians
- The principal issue on which the United States sought settlement with Great Britain at the outset of the War of 1812 was:
- guarantee of New England fishing rights off Newfoundland
- unrestricted navigation of the Mississippi River
- end to impressment
- cancellation of pre-Revolutionary War debts
- When President Thomas Jefferson stated in 1801, "We are all republicans; we are all democrats," he was referring to the:
- hope that principles of good government would transcend party politics
- exaggerated differences between his political theory and that of Alexander Hamilton
- array of political and social backgrounds present among his Cabinet appointees
- existing similarities between platforms of the Federalists and Democratic-Republicans
- In episodes such as Bacon's Rebellion, the Gaspee incident, the Boston Tea Party, and the Whiskey Rebellion, the violence:
- occurred because of the intervention of foreign powers in American internal affairs
- was directed at "outsiders" or representatives of distant authority
- subsided after the Articles of Confederation were replaced
- was largely confined to urban areas
- All of the following statements are consistent with the beliefs of Thomas Jefferson except:
- "the farmer is the backbone of American society"
- "freedom of speech is crucial in a republic"
- "an essential element to maintain orderly society is a strong national army"
- "the government is best that governs least"
- The Embargo Act of 1807:
- improved the balance of trade
- enriched many cotton plantation owners
- ruined American shipping
- virtually destroyed subsistence farming
- Alexander Hamilton's domestic and foreign policies were directed chiefly toward strengthening the federal government by:
- establishing gold as the sole foundation of United States currency
- advocating free trade
- favoring the interests of the propertied and monied classes
- averting American entanglement in Europe's wars
- In the case of Marbury v. Madison, the Supreme Court established that:
- states may not interfere with interstate commerce
- according to the implied powers clause, the issue of disputed electoral votes is a function of the Senate
- the Court has the authority to determine constitionality of congressional acts
- under certain circumstances, states have the authority to nullify laws of Congress
- The group most likely to oppose ratification of the Constitution was:
- farmers in isolated areas
- export merchants
- southern planters
- urban artisans
- To make the new government viable, the first Congress of the United States did all of the following except:
- organize a federal court system under the Supreme Court
- draft a bill of rights and send it to the states for ratification
- pass a tariff for the purpose of raising revenue
- grant subsidies to encourage industrial development
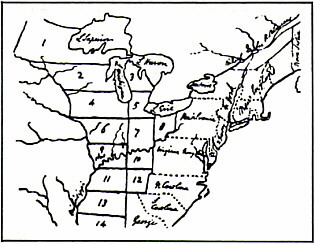
- The rough map above was used by Thomas Jefferson to:
- plot American strategy during the Revolutionary War
- give Lewis and Clark their instructions for exploration of the West
- begin surveying federal lands to later divide into new states
- plan a system of frontier fortifications
- The most notable achievement of the government under the Articles of Confederation concerned:
- establishment of separation of powers, including a bicameral legislature
- postwar economic prosperity
- systematic settlement of the vast western lands
- termination of America's participation in the international slave trade
- The Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions took the position that:
- only the United States Supreme Court had the power to limit freedoms of speech and press
- the authority of the state governments included the power to decide whether or not an act of Congress was constitutional
- only fiscal measures initiated by state legislatures could be acted on by Congress
- the "supremacy clause" of the Constitution applied only to foreign affairs
- The issue of constitutionality figured most prominently in the consideration of:
- the Whiskey Tax
- funding of the national debt
- the Bank of the United States
- assumption of state debts
- President George Washington's Farewell Address set a course for the nation by:
- endorsing the fledging two-party political system
- recommending strict term limits for elected federal officials
- warning against absolute separation of church and state
- discouraging permanent alliances with foreign governments
- The presidential election of 1800 has been referred to as constituting "another revolution" because:
- the House of Representatives decided the election
- voter turnout increased dramatically
- the party in power stepped down after losing the election
- Supreme Court action was required to dislodge the Federalists
- As originally ratified, the United States Constitution provided for:
- eventual elimination of slavery and bestowment of citizenship for blacks
- political parties, although it did not specify how many
- term limits for the major offices in all three branches of government
- election of the President by a system involving popular vote and formal electors
- The Hartford Convention was a manifestation of:
- opposition of New England Federalists to the War of 1812
- the War Hawks' discontent with President James Madison's foreign policy
- northern gratitude to General Andrew Jackson for his great victory at New Orleans
- westerners' outrage against Britain for backing Indian attacks on frontier settlements
- The statement that best describes the role that newspapers played in American politics during the late 1790s is:
- "newspapers expanded in number and circulation and, regardless of political perspective, were often guilty of libelous and irresponsible reporting"
- "although newspapers declined in circulation, their impact grew drastically owing to a new wave of public accountability and editorial responsibility"
- "newspapers declined in circulation and became chiefly the means for the socially elite to communicate among themselves from one pocket of society to another"
- "newspapers expanded in circulation but actually declined in influence because their focus tended to be matters of society hardly relevant to national interest and growth"
- The central government under the Articles of Confederation was denied power to:
- make treaties
- conduct diplomacy
- regulate Indian affairs
- levy taxes
- At the time of its completion, the Erie Canal was:
- the greatest construction project yet undertaken by Americans
- already obsolete due to the completion, in the meantime, of the Cumberland Road and the Baltimore & Ohio Railroad
- too poorly engineered to handle the current traffic flow
- long overdue as a replacement for slow and expensive railroads as the major means of shipment and passenger transportation in America
- The Sedition Act was enforced by the John Adams administration chiefly for the purpose of:
- keeping France from selling Louisiana to Spain
- barring illegal aliens from voting
- intimidating critics of the Adams foreign policy toward England and France
- protecting constitutional guarantees now threatened by the Democratic-Republicans
- President Thomas Jefferson overcame his doubts about the constitutionality of purchasing Louisiana from France because:
- timely Supreme Court decisions allowed him to proceed with actions that were originally denied to the President by the Constitution
- he decided that the guarantee of vast western land for American farmers outweighed constitutional principle
- his survey of the political landscape indicated that the action was crucial to his re-election hopes in 1804
- certain key provisions in the Pinckney Treaty were more broadly interpreted by Secretary of State James Madison, thus opening the door for the land acquisition
- In drafting the Articles of Confederation, the Continental Congress:
- was cautious about giving the new American government powers it had just denied Parliament
- granted the national court system the power to review both national and state laws
- was careful to establish division of powers among three separate branches of government
- gave Congress the important powers of controlling interstate commerce and raising revenue through taxation
- The statement that most accurately describes the attitude of the Founding Fathers toward political parties is:
- "parties are engines of democracy that provide citizens with a voice in government"
- "in a large republic, parties are the best means of creating effective coalitions of interest groups"
- "parties are vehicles of ambition and self interest that threaten the existence of a republican government"
- "a two-party system is essential to a stable republic"
- Great Britain's justification for its continued occupation of a number of posts located on United States soil despite the terms of the Treaty of Paris was that:
- the United States lacked the military capability to maintain the posts
- England's understanding with both France and Spain allowed the British to stay
- America had violated the treaty clauses dealing with the restoration of Loyalist property
- Great Britain needed a buffer zone between the United States and Canada
- The major reason why President Thomas Jefferson was interested in purchasing Louisiana from France was that he:
- hoped to preserve an agricultural society by making abundant lands available to future generations
- desired an area beyond the Mississippi River to relocate many eastern Indians
- wanted to establish a precedent for the expansion of presidential authority
- had learned from Lewis and Clark of the untapped mineral resources in western areas
- The status of Indians and tribes under the Constitution was:
- carefully clarified; Indian lands were ceded to the United States government and most Indians were restricted to reservations, either immediately or eventually
- unclear because tribes were considered legal entities but not foreign nations; furthermore, individual Indians were not granted United States citizenship
- to be determined by the state in which the tribe resided; each state was granted power to determine Indians' status most congruent with state interest
- subject to renegotiation because all treaties approved under the Articles of Confederation became null and void once the Constitution was ratified

- In the cartoon above, the snapping turtle represents the:
- refusal of Great Britain to conduct trade with the United States after the War of 1812
- general European reaction to the Treaty of Ghent
- adversarial relationship between America and Europe as a result of the Monroe Doctrine
- harmful effects of the 1807 Embargo Act
- The primary objection to the Constitution expressed by Samuel Adams, John Hancock, and other leading Anti-Federalists was that:
- it contained no absolute guarantees prohibiting abuse of basic civil liberties by government agents
- the federal government could conceivably suffer loss of power during periods of war and other inopportune times due to the so-called "elastic clause"
- the document was brief to the point of being incomplete, ignoring such important issues as additional statehoods, removal of the western Indians, and the question of slavery
- certain provisions were doomed to failure, such as the odd method of electing the President and the relative drastic lack of power allocated to the Supreme Court
- In the years prior to the War of 1812, both Great Britain and France violated American maritime neutral rights. The prime consideration causing the United States to declare war against Great Britain rather than France was:
- recent British transgressions had caused loss of American lives, whereas offenses committed by the French resulted in property damages only
- Canada, being adjacent to America, not only served as an avenue for attacking the British, but also as a potential prize of war (the only way to attack the French was to attack France itself; no French territory existed in North America worth the price of war for the United States)
- the Federalist Party, which controlled Congress, tended to be anti-British
- attacking France would almost certainly agitate Spain, as well (the United States stood a difficult challenge enough defeating one European nation; simultaneous war against both France and Spain would have been disastrous)
- The statement which best reflects the policy mandated by the Northwest Ordinance of 1787 with regard to slavery in the newly-created territories is:
- "the issue of slavery was not addressed"
- "each separate territory would determine, by vote of legal inhabitants, the question of slavery"
- "the decision of whether or not to allow slavery was left to the discretion of the individual inhabitants throughout the territories"
- "slavery was expressly prohibited"
|